A herniated disc, also known as a slipped disc, happens when the material inside the disc pushes through a damaged or weakened area of the spine. This can cause significant discomfort and affect mobility.
Do Bulging Discs Heal?
Several treatment options are available to help ease symptoms and promote recovery. However, recovery times can vary from person to person. Keep reading for more information on how long it may take for a herniated disc to heal and the available treatment options.
What is a Herniated Disc?
To understand herniated discs, it's helpful to first learn a bit about the spine's anatomy.
Spinal discs sit between the vertebrae, the bones that make up the spine. They act as shock absorbers, protect the spinal cord, and allow flexibility in the vertebral column.
The discs in the spine contain a soft material in the center called a nucleus, which is surrounded by a tough material called the annulus.
A herniated disc, also called a bulging disc, develops when a portion of the nucleus pushes through a weakened part of the annulus. Because of the displacement of the disc, it may press on the spinal nerves, causing pain and other symptoms.
Herniated discs can develop anywhere along the spine. However, they most commonly occur in the lumbar spine or lower back 1.
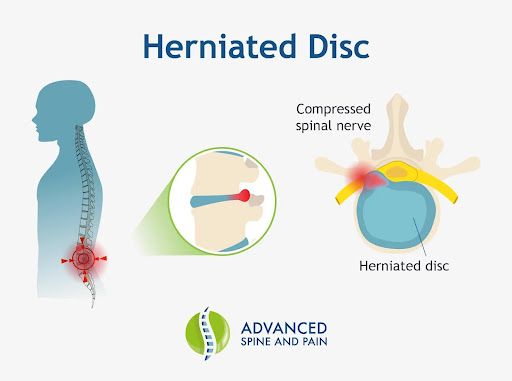
Symptoms of a Heated Disc
Bulging disc symptoms vary based on their location in the spine. Some symptoms include:
- Back or leg pain
- Numbness or tingling in the legs or feet
- Muscle weakness
- Reduced walking ability
If a bulging disc occurs in the cervical spine, symptoms may also include the following:
- Pain between or near the shoulder blades
- Pain that travels from the shoulder to the arm and possibly the fingers
- Neck pain, especially on the sides of the neck
- Pain that increases when bending or turning your neck
- Numbness or tingling in the arms
Complications of a Herniated Disc
Without treatment, it is possible for symptoms of a herniated disc to become worse. This can lead to chronic pain and decreased range of motion. In rare instances, a herniated disc can lead to severe complications.
Cauda equina syndrome, for example, is a rare emergency condition that occurs when a bundle of nerves at the base of the spine is damaged, leading to issues like difficulty urinating or incontinence. This condition requires urgent care.
Do Bulging Discs Heal?
Yes, most herniated discs heal on their own. In fact, this is the case for about 90% of cases2.
Self-healing may occur if the nucleus of the disc retracts back into the correct position and stops pushing into the spinal nerve canal. Usually, decreasing pain indicates healing.
How Long Does a Bulging Disc Take to Heal?
Herniated disc healing time may vary depending on the extent of the nerve involvement and the individual. For example, some patients have symptoms that resolve within a month3.
However, the complete recovery process can take anywhere from six to eight months4. It is also possible that the disc remains partially healed but does not cause any symptoms.
What Factors Affect How Fast A Herniated Disc Heals?
There are a few factors that can impact herniated disc healing time, including:
1) Severity of the herniation
Doctors may categorize a disc herniation as mild, moderate, or severe. They may classify the severity by the extent to which the inner part of the disc protrudes and the degree of nerve involvement. Often, the more severe the herniation, the longer it may take to heal.
2) Overall health
An individual's overall health also affects how fast they heal. For example, getting adequate rest and good nutrition may help with the healing process. Certain medical conditions and underlying diseases may slow healing.
3) Compliance with treatment
Once your physician recommends a treatment plan, adhering to the protocol is crucial to healing. For instance, following rehabilitation exercises or attending physical therapy as scheduled may determine how fast you heal.
Causes of a Herniated Disc
A herniated disc usually occurs due to gradual wear and tear associated with aging and disk degeneration. As individuals age, their discs become increasingly prone to tearing and rupturing.
Certain factors also increase the risk of developing a herniated disc, including:
- Being overweight
- Having a physically demanding job that involves repetitive pushing, pulling, and lifting
- Smoking, which may cause the disks to break down more quickly
- Being sedentary
Herniated Disc Treatment
Treatment for a herniated disc may involve non-surgical options or surgery. Initially, pain management is the focus, followed by conservative treatments, which can include a combination of the options listed below.
Non-surgical treatment
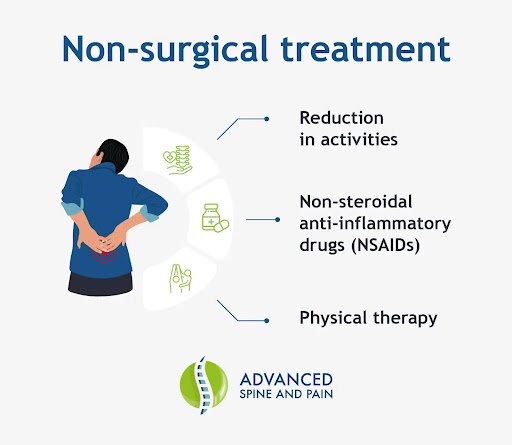
Doctors may recommend non-surgical treatment as the initial option. Non-surgical treatment may include:
- Reduction in activities: Although bed rest is usually not recommended, reducing activities that place additional stress on the disc can help decrease inflammation.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Pain medication, including anti-inflammatory medications, may help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Physical therapy: Ice and heat therapy, electrical muscle stimulation, ultrasound, and stretching exercises may reduce muscle spasms, improve muscle strength, and relieve pain.
- DISC Procedure: A DISC procedure is a non-surgical option involving injecting an allograft to supplement damaged discs. Additives to the injection include collagen, elastin, growth factors, and proteins. Once injected, the graph supports the disc's function, making it stronger.
Surgical treatment
If non-surgical options have not helped, surgery may be recommended. Spine surgery to treat a herniated disc may include minimally invasive surgical procedures or traditional surgery. Surgical options to treat a herniated disc include the folowing:
- LAND Procedure: A LAND procedure is a minimally invasive procedure that helps reduce compression and inflammation in the spinal cord. It involves using micro instruments to visualize and remove the damaged portion of the disc while leaving healthy tissue intact.
- LIFT (Lateral Interspinous Fusion Therapy) Procedure: A LIFT procedure is another alternative to traditional fusion surgery. The procedure involves using a Minuteman G3R MIS device to help stabilize the spine. This device provides stability comparable to rods and screws but with a less invasive approach. Because the procedure is minimally invasive, it allows for less blood loss, shorter operative time, and faster recovery.
- Artificial Disc Surgery: If other treatments have not helped, artificial disc surgery may be recommended. This surgery involves removing and replacing the damaged discs with an artificial or prosthetic disc. The procedure aims to reduce pain and restore normal mobility and functioning.
- Discectomy: Surgeons may use a discectomy to treat a herniated lumbar disc. The procedure involves removing all or part of the damaged disc to relieve pressure on the spinal cord. Depending on the location of the damaged disc, a discectomy may be performed using different approaches. Options include traditional open surgery, which involves larger incisions, and a minimally invasive procedure.
Can You Prevent a Bulging Disc?
It may not always be possible to prevent a herniated disc. However, you can decrease your risk by implementing some of the following tips:
- Use proper lifting form: Even a minor strain can lead to a herniated disc. When lifting, bend at the knees and maintain a straight back. Use leg muscles to lift. Maintain a healthy weight. Excess weight puts extra pressure on your back, including the spinal discs.
- Stretch regularly: Stretching daily can help keep the muscles surrounding the spine flexible, decreasing pressure on the discs.
- Maintain good posture: Good posture decreases strain on spines and may reduce the risk of a herniated disc. Good posture includes not slouching or rounding your shoulders, standing up tall, and engaging your core while sitting.
- Strength train: Regular exercise that strengthens your abdomen and back helps support the spine and maintain correct alignment.
- Avoid smoking: Cigarette smoke may weaken the discs in the spine, which makes them vulnerable to rupture.
Summary
If you have herniated disc symptoms, do not wait to seek treatment. Treatment options are available, including non-invasive procedures. If you have questions about treatment for herniated discs, we are happy to help.
To schedule an appointment, please contact Advanced Spine and Pain today!
Schedule an appointment online or contact us at 480-573-0130.
Sources
- Herniated Disc in the Lower Back. (2022). OrthoInfo. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/herniated-disk-in-th…
- Can Herniated Discs Heal on Their Own? ( 2024). Spine Health. https://www.spine-health.com/blog/can-herniated-discs-heal-their-own
- Herniated Discs. (2024). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12768-herniated-disk
- Can Herniated Discs Heal on Their Own? ( 2024). Spine Health. https://www.spine-health.com/blog/can-herniated-discs-heal-their-own

